Introduction:
REST (REpresentational State Transfer) is an architectural approach to design web services that are accessed using HTTP requests and verbs. It applies the architecture of the web to web service. In REST each resource is treated as a distinct resource and provides the functionality for bookmarking , caching etc. Depending on the use of HTTP verbs (GET, POST, DELETE, PUT) REST is divided into two types i.e. HI-REST and LO-REST.
In HI-REST it uses the verbs (GET, POST, DELETE, PUT) for a particular operations as the following way
GET : to fetch resource from server
POST: append to the resource
PUT:insert and update the resource
DELETE: to delete the resource
But in the case of LO-REST POST verb is used for insert, update, delete and fetch of the resource.
Implementation:
Implementation:
Microsoft .net framework introduces a binding called webHttpBinding in Windows Communication Foundation(WCF) for creating and consuming REST based web services. To create a REST based web service we have to follow the below processes.
- We have to decorate the operation contracts we have defined in our service interface either with WebGet or WebInvoke attribute to make it REST enable (to access this attribute we have to reference System.ServiceModel.Web namespace)
- Set the binding of endpoint to webHttpBinding in the configuration file.
- Add a behavior under the endPointBehaviors element that has a webHttp child element
- Add a behavior configuration to your endpoint that references the endpoint behavior.
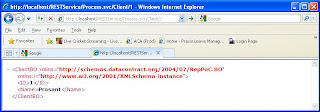
When we are using the WebGet attribute the method to access the service method is GET. So we can access it from any browser using the URL like http://localhost/RESTTest/ClientService.svc/Clients/
But when we use the WebInvoke attribute to decorate our operation contract to make it REST enable we have to specify the method of accessing it (i.e. GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
Example of Service Interface :
[ServiceContract]
public interface IProcess
{
[OperationContract, WebInvoke(BodyStyle = WebMessageBodyStyle.Bare, Method = "GET",
RequestFormat = WebMessageFormat.Xml, ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Xml, UriTemplate = "Client/{clientID}")]
ClientBO Process(string clientID);
[OperationContract, WebGet(BodyStyle = WebMessageBodyStyle.Bare,
RequestFormat = WebMessageFormat.Xml, ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Xml, UriTemplate = "Clients/")]
IEnumerable<ClientBO> Process1();
[OperationContract, WebInvoke(BodyStyle = WebMessageBodyStyle.Bare, Method = "POST",
ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Xml, UriTemplate = "AddClient/")]
bool AddClient(Stream client);
}
Configuration File Setting:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<system.web>
<compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.0" />
</system.web>
<system.serviceModel>
<services>
<service name="RepPoC.RESTService.Process">
<endpoint address="" binding="webHttpBinding" contract="RepPoC.RESTService.IProcess"
behaviorConfiguration ="WebBehavior" />
</service>
</services>
<behaviors>
<endpointBehaviors>
<behavior name="WebBehavior">
<webHttp />
</behavior>
</endpointBehaviors>
</behaviors>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
Code to Call REST Service:
//GetSerializedData basically takes your object as parameter and serialize it and return the byte array. We need to pass it
//with request
Byte[] postData = GetSerializedData(client);
WebRequest request = WebRequest.Create(new Uri("http://localhost/RESTService/Process.svc/AddClient/"));
request.Method = "POST";
request.ContentLength = postData.Length;
request.ContentType = "text/plain";
Stream postStream ;
postStream = request.GetRequestStream();
postStream.Write(postData, 0, postData.Length );
WebResponse response = request.GetResponse();
StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(response.GetResponseStream());
Response.Write(reader.ReadToEnd());
Advantages of REST:
- Provides improved response time and reduces server load due to it's support of caching
- Improves server scalability by reducing the need of maintaining session state
- Does not require a separate resource discovery mechanism , due to the use of hyperlink in representation
- Network admin can easyly understand what operation is going on the server by looking the URLs
- Easier to use compared to SOAP based services.
- Lightweight - Output are in plain XML, not extra markup in output like SOAP
- REST is certainly not a replacement for Web services, as it doesn’t provide the
breadth of features like security, quality of service, transactions, queuing etc. - Doesn't provide any metadata. The user has implicitly know what a service requires.